Sepsis is a word that tends to evoke concern, but many people aren’t aware of just how serious this condition can be. Imagine your body’s response to an infection spiraling out of control, leading to widespread inflammation and potential organ failure. It’s not something we typically think about until it strikes close to home. Understanding the symptoms of sepsis can be life-saving.
In this ultimate guide, we’ll delve into what sepsis is, explore its causes and risk factors, and highlight the critical signs you should never ignore. With knowledge comes power—power to recognize when something is wrong and act swiftly. Whether for yourself or a loved one, being informed can make all the difference in navigating through this medical emergency. Let’s unravel the complexities surrounding sepsis together!
What is Sepsis?
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition triggered by the body’s extreme response to an infection. It occurs when the immune system goes into overdrive, leading to widespread inflammation throughout the body.
This inflammatory response can cause blood flow issues, depriving essential organs of oxygen and nutrients. As a result, vital body functions may begin to fail. Sepsis can develop from various infections, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, or even skin infections.
Anyone can be affected by sepsis; however, it is particularly dangerous for young children, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems. The rapid progression of sepsis makes it crucial to recognize its symptoms early on. Understanding what sepsis is enables you to respond effectively if faced with this medical emergency.
Causes of Sepsis
Sepsis arises when the body’s response to infection spirals out of control. This can happen due to various types of infections, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, or abdominal infections.
Bacteria are often responsible, but viruses and fungi can also trigger sepsis. When these pathogens invade the bloodstream, they release toxins that lead to widespread inflammation.
Certain medical procedures may increase susceptibility as well. Surgical operations or invasive devices like catheters put patients at higher risk for developing infections that could culminate in sepsis.
Additionally, chronic health conditions such as diabetes and liver disease make individuals more vulnerable. The immune system’s ability to fight off infections weakens over time with age too.
Understanding these causes is crucial in preventing severe complications associated with this life-threatening condition.
Risk Factors for Developing Sepsis
Certain individuals are more vulnerable to sepsis due to various risk factors. Age plays a significant role; both the very young and older adults have weakened immune systems, making them more susceptible.
Chronic health conditions like diabetes, cancer, or liver disease can also increase the likelihood of developing sepsis. These pre-existing conditions may impair the body’s ability to fend off infections effectively.
Additionally, hospital stays or recent surgeries elevate risks significantly. Invasive procedures can introduce pathogens into the bloodstream.
Immunosuppressive medications further contribute to this vulnerability. Patients on steroids or chemotherapy often face higher chances of severe infections leading to sepsis.
Lifestyle choices shouldn’t be overlooked. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken overall health and immunity. Awareness of these factors is key in recognizing potential threats early on.
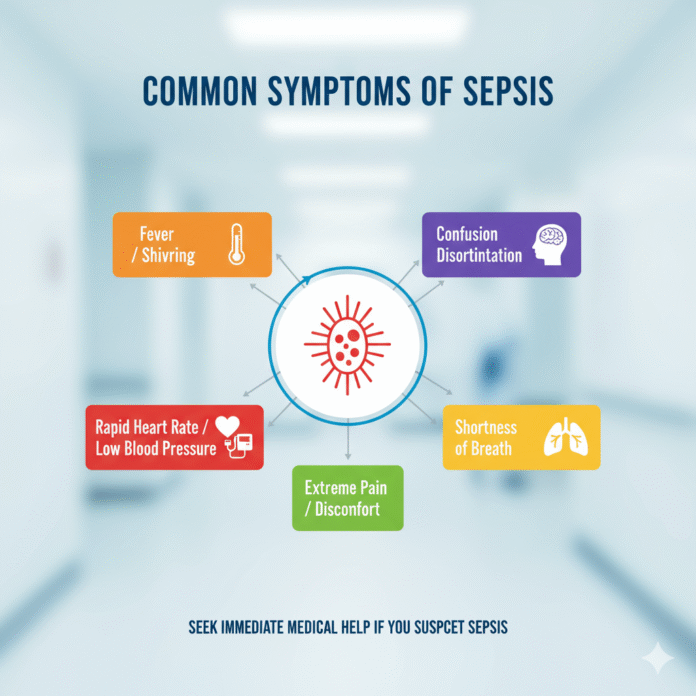
Signs and Symptoms of Sepsis
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of sepsis is crucial for prompt treatment. This serious condition often starts with a simple infection that spirals out of control.
Common early symptoms include fever, chills, or a sudden drop in body temperature. Rapid breathing and heart rate are also indicators that something isn’t right.
Patients may feel confused or disoriented. This mental fog can escalate quickly, making it hard to think clearly.
Skin changes can occur as well. Look for mottled skin or rashes that don’t fade under pressure. These physical signs signal severe distress within the body.
Fatigue is often overwhelming. A person may feel unusually weak or lethargic, even after adequate rest.
If you notice these symptoms in yourself or someone else, seek medical help immediately. Timely intervention can make all the difference in outcomes related to sepsis.
Understanding the Stages of Sepsis
Sepsis progresses through distinct stages, each with varying severity. Initially, there’s sepsis, characterized by a systemic inflammatory response to infection. At this stage, the body releases chemicals into the bloodstream to fight off pathogens.
As it advances, severe sepsis occurs. Here, organ functions begin to deteriorate due to inadequate blood flow and oxygen delivery. Symptoms can escalate quickly during this phase.
The most critical level is septic shock. This situation arises when blood pressure drops dangerously low despite treatment efforts. Vital organs suffer from insufficient circulation and may start failing rapidly.
Recognizing these stages early is crucial for effective intervention. Timely medical attention can drastically improve outcomes for those affected by sepsis. Understanding these progressions empowers both patients and healthcare providers in addressing this serious condition effectively.
How is Sepsis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing sepsis is a critical process that begins with a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. Doctors often look for signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or rapid heart rate.
Laboratory tests play an essential role in confirming sepsis. Blood samples are taken to check for bacteria or other pathogens. A complete blood count (CBC) can reveal changes in white blood cell levels indicating an infection.
Imaging studies may also be employed to identify sources of infection within the body. X-rays, ultrasounds, or CT scans can help pinpoint issues like pneumonia or abscesses.
Healthcare providers might use specific criteria known as the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score to evaluate organ function and overall severity. Timely diagnosis is crucial since early intervention significantly improves outcomes for individuals battling this serious condition.
Treatment Options for Sepsis
When it comes to treating sepsis, timely intervention is crucial. Healthcare providers typically start with intravenous antibiotics to combat the underlying infection. Administering these medications as soon as possible can significantly improve outcomes.
Fluid replacement is another essential treatment option. This helps maintain blood pressure and ensures vital organs receive adequate oxygen and nutrients. In many cases, patients may also require medications known as vasopressors to stabilize their blood pressure.
In advanced cases of sepsis or septic shock, more intensive measures might be necessary. This could involve mechanical ventilation for respiratory support or even dialysis if kidney function declines.
Additionally, addressing the source of infection is critical; this might mean surgery to remove infected tissue or drainage procedures for abscesses. Every case presents unique challenges that healthcare teams must navigate carefully and swiftly.
Prevention and Awareness
Preventing sepsis starts with understanding its origins. Good hygiene practices can significantly reduce the risk of infections that may lead to this life-threatening condition. Regular handwashing, especially before meals and after using the restroom, is essential.
Vaccinations play a crucial role too. Staying up-to-date on immunizations can protect against diseases known to cause sepsis. This proactive approach is vital, particularly for vulnerable populations.
Awareness in communities fosters education about recognizing symptoms early. Symptoms like fever, increased heart rate, or confusion are red flags requiring immediate attention. Training local healthcare professionals and families on these signs helps save lives.
Encouraging open conversations about health concerns empowers individuals to seek timely medical help when needed. Early intervention remains key in managing potential cases of sepsis effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms of sepsis is crucial for early detection and treatment. This life-threatening condition can escalate rapidly, making awareness essential. Recognizing the signs, such as fever, confusion, increased heart rate, or difficulty breathing, can be lifesaving.
Sepsis affects people differently based on various factors including age and underlying health conditions. By knowing who is at higher risk and what to look out for in terms of symptoms, you empower yourself and others to seek medical help promptly.
Diagnosis typically involves tests that assess organ function and identify infections. Treatment often requires hospitalization where intravenous fluids and antibiotics are administered swiftly to combat infection.
Prevention strategies also play a vital role in reducing sepsis cases. Simple actions like maintaining good hygiene and getting vaccinated against certain infections can make a significant difference.
Awareness leads to action—yours may just save a life. Stay informed about the symptoms of sepsis so you can act fast when it matters most.