CVA medical, or cerebrovascular accident, is a term that often sends shivers down the spine. For many, it conjures images of sudden strokes and unexpected hospital visits. But what exactly does CVA mean for you or your loved ones? Understanding this critical health issue can be life-changing.
In this guide, we delve into the intricacies of CVA medical—from its various types to symptoms and treatment options. Whether you’re seeking knowledge for yourself or supporting someone else on their journey, we’ve got you covered. Let’s explore how to recognize the signs early, manage risks effectively, and make lifestyle adjustments that promote better brain health. Your awareness today could lead to a healthier tomorrow!
Understanding CVA Medical
CVA medical refers to cerebrovascular accidents, commonly known as strokes. This condition occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, leading to tissue damage and potential loss of function.
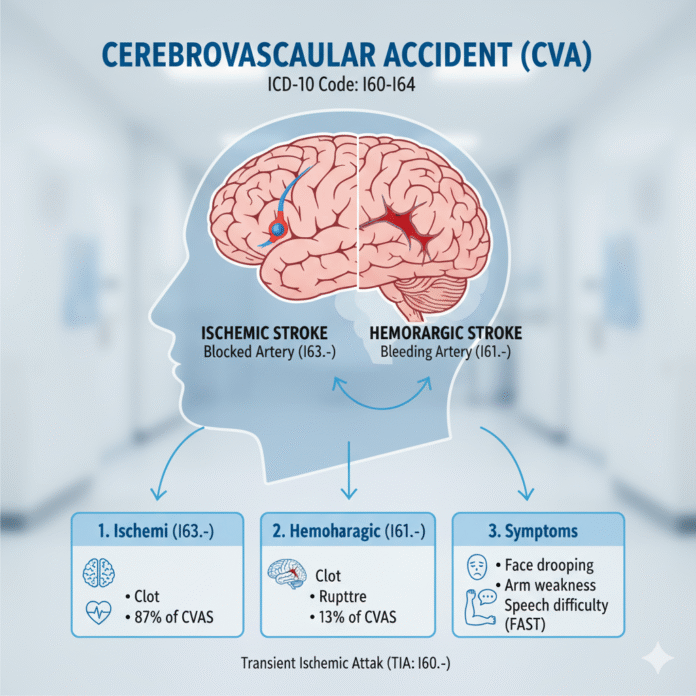
There are two primary types: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes result from blocked arteries, often due to clots. Hemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood vessel bursts, causing bleeding in or around the brain.
Understanding CVA is vital because time is crucial during these events. The sooner someone receives treatment, the better their chances of recovery.
Awareness of risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes can aid prevention efforts. Knowing how lifestyle choices impact your health can empower you to take proactive steps toward reducing your risk for CVA medical issues down the line.
Different Types of CVA
Cerebrovascular accidents, commonly known as CVAs or strokes, can be categorized primarily into two types: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
Ischemic strokes occur when a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain becomes blocked. This blockage may result from a clot or a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. Such conditions are often linked to high cholesterol and hypertension.
On the other hand, hemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures. This leads to bleeding within or around the brain tissue. Common causes include high blood pressure and aneurysms that weaken arterial walls.
Another type worth mentioning is transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). Often called “mini-strokes,” TIAs produce similar symptoms but last for only a short time without causing permanent damage. They serve as critical warning signs for future strokes if not addressed promptly.
Symptoms and Causes of CVA
CVA, or cerebrovascular accident, commonly known as a stroke, presents with various symptoms that often arise suddenly. People may experience numbness or weakness in the face, arms, or legs—typically on one side of the body.
Sudden confusion is another alarming sign. This can manifest as difficulty speaking or understanding language. A person might also struggle to walk and have issues with coordination and balance.
The causes of CVA are multifaceted. The most prevalent type is ischemic stroke, caused by a blockage in blood vessels leading to the brain. This disruption deprives brain cells of oxygen and nutrients.
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel ruptures within the brain. High blood pressure can elevate this risk significantly.
Other contributing factors include diabetes, high cholesterol levels, obesity, smoking habits, and excessive alcohol consumption—all vital areas for awareness and prevention.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for CVA
Diagnosing a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) requires prompt medical attention. Healthcare professionals typically perform a physical examination and review the patient’s medical history. Imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs are crucial for identifying the type and location of the stroke.
Treatment options vary based on whether the CVA is ischemic or hemorrhagic. For ischemic strokes, medications such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) can help dissolve blood clots. Hemorrhagic strokes may necessitate surgical interventions to repair damaged blood vessels.
Rehabilitation plays an essential role in recovery. This often involves physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech-language pathology to regain lost functions. Support from healthcare teams helps patients navigate their journey toward healing while addressing emotional challenges that may arise during recovery.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent CVA
Making mindful lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of CVA. Start with your diet. Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while cutting back on saturated fats and sugars.
Regular physical activity is crucial too. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. This helps maintain a healthy weight and promotes cardiovascular health.
Don’t underestimate the power of stress management techniques like meditation or yoga. These practices can lower blood pressure and improve overall well-being.
Quitting smoking is another vital step. The chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels, increasing your stroke risk.
Keep regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor conditions like hypertension or diabetes that could lead to CVA if left unmanaged. Taking these proactive steps creates a solid foundation for long-term heart health.
Support and Resources for Those with CVA
Support is crucial for individuals affected by CVA. Various organizations offer resources tailored to their needs, providing both emotional and practical assistance.
Local support groups can create a sense of community. These gatherings allow patients and families to share experiences, fostering understanding and connection. Many find comfort in knowing they are not alone on this journey.
Online platforms also play an essential role. Websites dedicated to stroke recovery provide valuable information about rehabilitation, coping strategies, and adaptive technologies. Forums enable users to ask questions and receive advice from others who have faced similar challenges.
Healthcare providers often recommend therapy services focused on physical, occupational, or speech rehabilitation. Personalized programs help regain lost skills while boosting confidence.
Families benefit from educational materials that enhance their understanding of CVA care. This knowledge empowers them to assist loved ones effectively during recovery efforts.
Conclusion
CVA medical, or cerebrovascular accident, is a serious condition that affects countless individuals each year. Understanding the nature of CVAs and their various types can empower patients and their families to recognize symptoms early on. This knowledge can be crucial in seeking timely medical intervention.
Awareness of the causes behind CVA helps highlight risk factors. For many, lifestyle changes such as improved diet and regular exercise are essential steps toward prevention. Engaging in healthy habits not only reduces risks but also enhances overall well-being.
Accessing proper diagnosis and treatment options enables those affected to manage their condition effectively. A range of therapies exists, from medications to rehabilitation programs designed specifically for recovery post-CVA.
Support networks play an invaluable role for both patients and caregivers navigating this challenging journey. Resources are available through healthcare providers, community organizations, and online platforms dedicated to providing assistance.
Understanding CVA medical is just the first step—taking action towards prevention and management makes all the difference in maintaining a healthier future for everyone involved.