Pleural effusion is a medical condition that can catch many off guard. Imagine feeling unwell, struggling to breathe, yet not knowing the underlying issue. This fluid buildup in the pleural space—the area between your lungs and chest wall—can lead to various health complications if left untreated. With increasing awareness about respiratory issues, understanding pleural effusion becomes essential for both patients and healthcare providers alike.
In this blog post, we will dive into what pleural effusion really means, explore its causes and symptoms, discuss how it’s diagnosed using ICD-10 codes, outline treatment options available today, and finally touch on preventive measures to reduce recurrence. Whether you’re seeking knowledge for yourself or a loved one, this comprehensive guide aims to shed light on an often-overlooked topic in respiratory health. Let’s embark on this journey of discovery!
Understanding Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity, which surrounds your lungs. This space typically contains a small amount of fluid that helps lubricate and facilitate lung movement during breathing.
When the body produces too much fluid or fails to absorb it properly, this balance is disrupted. The result can be discomfort and difficulty breathing, depending on the volume of fluid present.
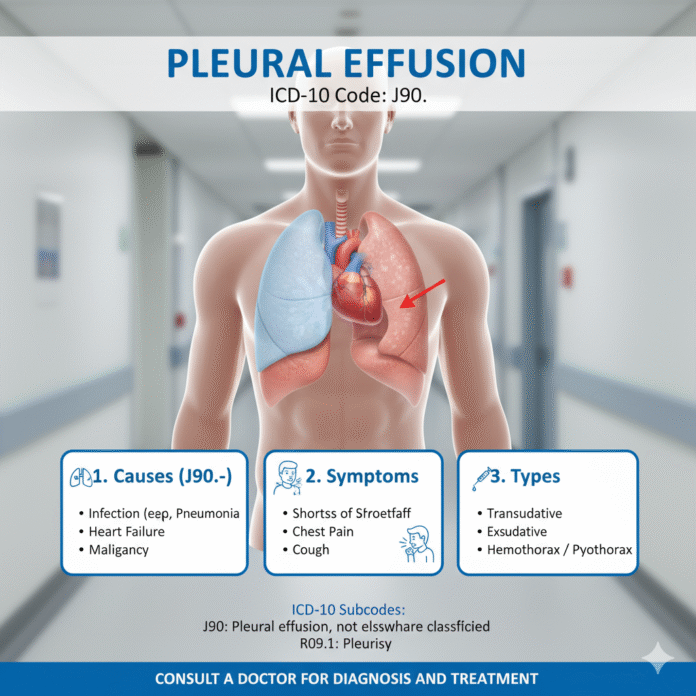
The condition may arise from various underlying health issues. Infections, heart failure, or malignancies are common culprits. However, not all cases manifest symptoms right away.
While some individuals remain unaware they have pleural effusion until diagnosed through imaging tests like chest X-rays or ultrasounds, others may experience noticeable signs such as shortness of breath or chest pain. Awareness is key to addressing this condition effectively before it escalates into more serious complications.
Causes and Symptoms of Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity, which is the space between the lungs and chest wall. Various factors can lead to this condition. Common causes include heart failure, pneumonia, cancer, and pulmonary embolism.
Patients may not always notice symptoms initially. As fluid builds up, they might experience shortness of breath or a persistent cough. Chest pain can also occur, particularly when breathing deeply or coughing.
Other signs may involve fever if an infection is present or increased respiratory rate due to discomfort.
Understanding these aspects helps in identifying potential cases early on and addressing them promptly with medical attention. Being aware of these triggers can be crucial for those at risk.
Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion
Diagnosing pleural effusion begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers often listen for abnormal sounds in the lungs, which may indicate fluid buildup.
Imaging tests play a crucial role. A chest X-ray can reveal large amounts of fluid, while ultrasound offers more detailed insights into the pleural space. These tools help determine both the presence and size of the effusion.
In some cases, further evaluation is necessary to understand the underlying cause. A CT scan provides enhanced visibility and detail that may not be apparent through standard imaging methods.
Doctors might perform a thoracentesis—a procedure where they extract fluid from the pleural cavity using a needle. Analyzing this fluid can uncover essential information about its composition and origin, guiding appropriate treatment options moving forward.
ICD-10 Codes for Pleural Effusion
The ICD-10 coding system is essential for classifying various medical conditions, including pleural effusion. These codes help healthcare providers communicate effectively about diagnoses and ensure accurate billing.
For pleural effusion, the primary code is J90. This code represents a nonspecific accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity without detailing its cause or nature.
If the effusion has an underlying condition, additional codes may apply. For instance, if it results from heart failure or pneumonia, those specific diagnoses should be coded alongside J90 to provide a complete picture.
Understanding these codes assists in tracking prevalence and treatment outcomes for patients with pleural effusion across different healthcare settings. Accurate coding also enhances research on this condition’s impact on public health and resource allocation.
Treatment Options for Pleural Effusion
Treatment for pleural effusion often begins with addressing the underlying cause. Identifying whether it’s due to infection, heart failure, or malignancy is crucial.
If fluid accumulation is significant, a doctor may perform thoracentesis. This procedure involves inserting a needle into the pleural space to remove excess fluid, providing immediate relief.
For recurring cases, more invasive measures like placement of a chest tube might be necessary. This allows continuous drainage and helps prevent re-accumulation.
In some instances, medication can help manage symptoms or treat specific conditions that lead to effusions. For example, diuretics may assist in reducing fluid buildup related to heart issues.
Surgical interventions may also be considered for chronic effusions or when malignant causes are involved. Procedures such as pleurodesis aim to adhere the lung surface to the chest wall and minimize future fluid collections.
Preventing Recurrence of Pleural Effusion
Preventing a recurrence of pleural effusion involves addressing the underlying causes. For those with chronic conditions, managing diseases such as heart failure or cancer is essential.
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role. Maintaining a healthy weight and following a balanced diet may help reduce fluid buildup in the chest cavity. Staying active, within medical advice, encourages better lung function and circulation.
Regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring health status. Engaging with healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans can aid in preventing future occurrences.
Diuretics might be prescribed to control fluid retention effectively. Adhering to medication regimens ensures that any potential flare-ups are managed promptly.
In cases related to infections or inflammation, follow-up care should not be overlooked. Timely intervention helps minimize risks associated with recurring pleural effusions and enhances overall well-being.
Conclusion
Pleural effusion is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual’s health. Understanding its causes and symptoms is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. With the right approach, including awareness of ICD-10 codes related to pleural effusion, healthcare providers can streamline the process of care.
Treatment options vary based on the underlying cause but often involve medication or procedures to remove excess fluid. Preventative measures play a critical role in reducing recurrence rates, allowing patients to manage their conditions more effectively.
Awareness and education about pleural effusion are key components in navigating this medical challenge. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms yourself or supporting someone who is, having access to accurate information can make all the difference in achieving better health outcomes.