Overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition that affects millions of people around the world, yet it often remains shrouded in misunderstanding and stigma. Imagine feeling an urgent need to urinate at the most inconvenient times or rushing to find a restroom when you least expect it. This can be more than just an inconvenience; it can significantly impact daily life and mental well-being.
If you’ve been experiencing these symptoms, it’s essential to understand both your body and how health professionals classify this condition. One critical aspect is understanding how OAB is documented in medical terms through coding systems like ICD-10. Knowing about overactive bladder ICD 10 codes can help facilitate conversations with healthcare providers, streamline treatment options, and ultimately lead to better management of this bothersome condition. So let’s dive deeper into what overactive bladder entails and explore ways to reclaim control over your life!
Understanding Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder is more than just frequent trips to the bathroom. It’s a chronic condition that causes an overwhelming urge to urinate, often accompanied by incontinence. This urgency can disrupt daily activities and lead to anxiety about finding restrooms.
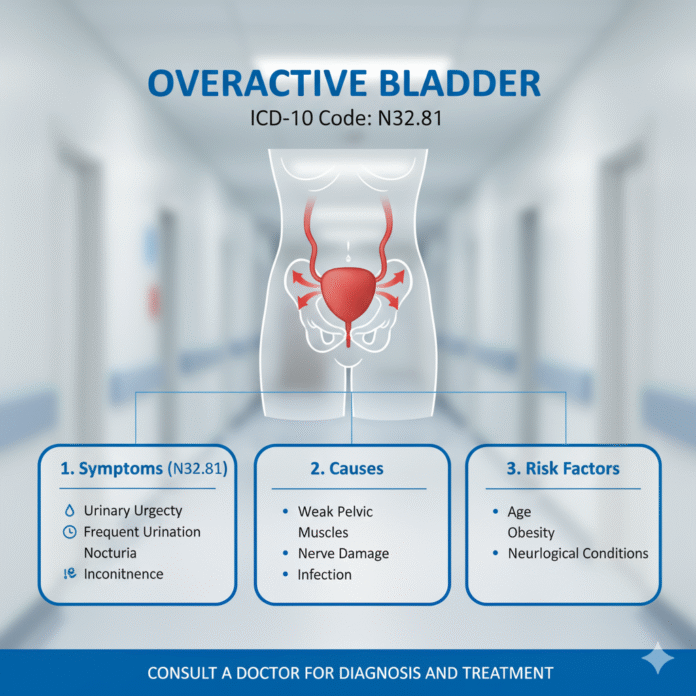
The exact cause of OAB isn’t always clear. It may stem from muscle dysfunction in the bladder or nerve issues that interfere with normal signaling. Factors like age, certain medications, and underlying health conditions can also play a role.
Men and women experience OAB differently, but both can find it challenging. Understanding these nuances helps foster conversations around treatment options available for those impacted. Awareness is the first step toward effective management strategies tailored to individual needs.
What is ICD-10?
ICD-10, or the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, is a coding system used by healthcare providers worldwide. It offers a standardized approach to documenting and classifying diseases and health conditions.
Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), ICD-10 encompasses thousands of codes that cover various medical diagnoses. This classification aids in accurate reporting and ensures consistency across different healthcare settings.
Healthcare professionals utilize these codes for billing purposes, research, and epidemiological studies. By employing ICD-10 codes, providers can track disease prevalence more effectively.
The transition from earlier versions to ICD-10 marked significant improvements in detail and specificity. This change allows clinicians to better understand patient demographics while streamlining treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
The ICD-10 Code for Overactive Bladder
The ICD-10 code for overactive bladder is N32.81. This classification helps healthcare providers accurately document and diagnose the condition.
Using this specific code ensures that insurance claims are processed efficiently. It allows healthcare practitioners to communicate effectively about a patient’s symptoms, treatment plans, and outcomes.
Patients may find it useful to understand their diagnosis in terms of coding. It can help them take an active role in discussions with their doctors.
Proper coding also contributes to research and statistics on overactive bladder prevalence. This information is vital for improving treatments and resources available for those affected by the condition.
In essence, knowing the ICD-10 code empowers both patients and professionals alike while navigating the complexities of medical care.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder presents a range of distinct symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. The most common sign is a frequent urge to urinate, often accompanied by an inability to delay the urge. This urgency can occur unexpectedly and may lead to involuntary leakage.
Many individuals also experience nocturia, which means waking up multiple times during the night to urinate. This disrupts sleep patterns and contributes to fatigue throughout the day.
Diagnosis typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers may conduct urine tests or bladder diaries, where patients track their symptoms over time.
In some cases, urodynamic testing might be recommended for further evaluation of bladder function. Understanding these symptoms is key in seeking appropriate treatment options tailored for managing this condition effectively.
Treatment Options for Overactive Bladder
Treatment for overactive bladder varies based on the severity of symptoms and individual needs. Medications are often a first line of defense. Anticholinergics can help reduce urgency and frequency by calming the bladder muscles.
For those who don’t respond well to medications, nerve stimulation therapies may offer relief. Sacral neuromodulation involves implanting a small device that sends signals to the nerves controlling the bladder.
In some cases, Botox injections in the bladder wall are an option. This reduces muscle contractions and increases storage capacity.
Behavioral therapies play a crucial role too. Bladder training techniques help individuals regain control by gradually increasing intervals between bathroom visits.
Surgical options exist for persistent cases. These procedures aim to either increase bladder capacity or improve sphincter function, providing long-term solutions for affected patients.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Overactive Bladder
Making small adjustments to your daily routine can significantly impact managing overactive bladder symptoms. Start by tracking your fluid intake. Limit caffeine and alcohol, as these can irritate the bladder.
Incorporating regular physical activity into your life is also beneficial. Aim for gentle exercises like walking or yoga, which help strengthen pelvic muscles and improve overall function.
Establishing a bathroom schedule may provide structure. Try to urinate at set intervals rather than waiting for the urge to arise.
Diet plays a crucial role too. Opt for fibers that promote healthy digestion while avoiding spicy foods that might trigger urgency.
Consider practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation. Stress management can reduce episodes associated with anxiety and nervousness related to bladder control issues.
Conclusion
Overactive bladder is a condition that can significantly affect daily life. Understanding its ICD-10 code helps healthcare providers accurately diagnose and treat the issue. By recognizing symptoms early, patients can seek appropriate care.
There are various treatment options available, ranging from medication to lifestyle changes. Implementing simple adjustments in daily habits may also provide relief for those struggling with this condition.
With awareness and management strategies, individuals facing overactive bladder can reclaim control of their lives. Seeking professional guidance ensures that each person receives tailored support for their journey toward improvement.