Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. It attacks the liver and can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Understanding how hepatitis B is transmitted is crucial for safeguarding your health and the well-being of others. With awareness, we can break down barriers, dispel myths, and promote better practices to prevent its spread. Let’s dive into what you need to know about this virus, including transmission methods, high-risk groups, symptoms, and the importance of vaccination in combating this public health issue.
How is Hepatitis B Transmitted?
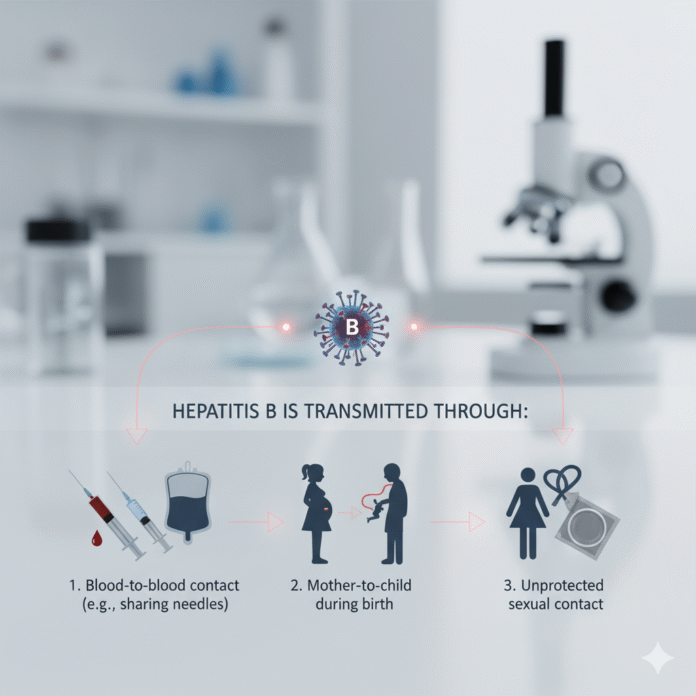
Hepatitis B is primarily transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids. This includes blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
One common way the virus spreads is through unprotected sexual intercourse. Engaging in sex without a barrier can put individuals at risk.
Sharing needles or syringes also poses a significant threat. Drug users who share equipment increase their likelihood of exposure to Hepatitis B.
In addition, transmission can occur from mother to child during childbirth. An infected mother may pass the virus to her baby during delivery.
Household items like toothbrushes or razors that come into contact with blood can be another route for infection.
Healthcare settings are not exempt either; improper handling of medical instruments could lead to transmission as well. Understanding these pathways helps highlight the importance of preventative measures.
High-Risk Groups for Hepatitis B Transmission
Certain groups are more vulnerable to hepatitis B transmission. Understanding these populations is crucial for effective prevention strategies.
Individuals who engage in unprotected sexual activities with multiple partners face a higher risk. The virus can easily spread through bodily fluids during intercourse.
Injection drug users are another significant group at risk. Sharing needles or other equipment increases the likelihood of contracting hepatitis B, as the virus lives in blood.
Healthcare workers must also be vigilant. They often encounter situations where exposure to infected blood could occur, making safety protocols essential.
Additionally, newborns born to mothers with hepatitis B have a high chance of infection if not properly vaccinated at birth. Addressing this issue early on can help curb future cases within families and communities.
People living in regions with high prevalence rates should take extra precautions and get regularly tested for their health’s sake.
Symptoms and Complications of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B often presents with mild symptoms that can be easily overlooked. Many individuals may experience fatigue, loss of appetite, and occasional nausea. These initial signs can feel like a common flu or viral infection.
As the virus progresses, jaundice might set in. This condition causes yellowing of the skin and eyes due to liver dysfunction. Dark urine and pale stools are also telltale indicators.
Complications arise when chronic hepatitis B goes untreated. The risk of cirrhosis increases over time, leading to severe scarring of the liver. In some cases, this can progress to liver cancer.
Regular monitoring is crucial for those diagnosed with hepatitis B. Understanding these symptoms helps facilitate timely medical intervention before serious complications develop.
The Importance of Prevention and Vaccination
Preventing the spread of hepatitis B is crucial in safeguarding public health. Vaccination stands out as one of the most effective methods to achieve this goal.
The hepatitis B vaccine offers strong protection against infection. It stimulates the immune system, equipping it to combat the virus effectively if exposed. This proactive approach significantly reduces transmission rates.
Education plays a vital role too. Many people remain unaware that they are at risk or unvaccinated. Public awareness campaigns can help bridge this knowledge gap, encouraging individuals to seek vaccination and understand safe practices.
Routine screenings for high-risk groups also contribute to prevention efforts. Identifying infections early can prevent further transmission and improve long-term outcomes for those affected.
By fostering an environment focused on prevention and education, communities can work together to reduce hepatitis B prevalence and ensure healthier futures for all individuals.
Treatment Options for Hepatitis B
Treatment for hepatitis B varies depending on the stage of the infection. For acute cases, healthcare providers often recommend monitoring without immediate intervention. Many individuals recover naturally.
For chronic hepatitis B, antiviral medications are available. These can help reduce viral load and improve liver function. Common drugs include tenofovir and entecavir, both effective in managing the virus.
In specific situations, pegylated interferon may be prescribed to boost the immune response against hepatitis B. This treatment requires careful management due to potential side effects.
Regular check-ups are crucial for anyone undergoing treatment. Monitoring liver health helps detect complications early. Lifestyle changes also play a significant role; maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcohol support overall well-being during treatment.
It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to choose the best approach based on individual circumstances and needs.
Stigma and Misconceptions Surrounding Hepatitis B
Stigma around hepatitis B can create significant barriers for those affected. Many people associate the virus with risky behavior, leading to discrimination and isolation.
Misconceptions abound regarding its transmission. Some believe it spreads through casual contact, like hugging or sharing utensils. This misinformation fuels fear and misunderstanding in communities.
Individuals living with hepatitis B often face unwarranted judgment from friends and family. Such stigma can deter them from seeking medical care or discussing their status openly.
Education is crucial in dispelling these myths. By understanding how hepatitis B is transmitted, we can foster a more compassionate environment.
When we challenge negative perceptions, we empower individuals to seek treatment without shame—creating a supportive community where everyone feels safe and understood.
Conclusion: Spreading Awareness and Taking Action to Combat the Transmission of Hepatitis B
Awareness and education are key components in the fight against hepatitis B. Understanding how hepatitis B is transmitted can empower individuals to take necessary precautions. Sharing knowledge about transmission routes not only helps prevent new infections but also reduces stigma faced by those living with the virus.
Vaccination remains one of the most effective tools we have. It’s crucial for high-risk groups, as well as pregnant women, to get vaccinated and protect themselves and their families from this potentially serious virus.
Encouraging regular testing and open discussions about sexual health can further reduce transmission rates. Healthcare providers play a vital role in informing patients about their risks and offering guidance on prevention strategies.
By coming together as a community, advocating for more resources, and supporting those affected by hepatitis B, we pave the way for a healthier future where fewer people suffer from its consequences. Spreading awareness is our collective responsibility; let’s unite to combat this public health challenge effectively.