Imagine a long, painful journey that starts in water and ends inside your body. It’s not the plot of a horror movie; it’s the reality for those affected by guinea worm dracunculiasis. This ancient disease has plagued humanity for centuries, leaving behind stories of suffering and resilience. Today, we delve into what guinea worm dracunculiasis really is—its history, how it spreads, symptoms to look out for, treatment options available, and efforts underway to eradicate this debilitating affliction once and for all. Join us as we explore this captivating yet challenging aspect of public health!
Definition and History of Guinea Worm Dracunculiasis
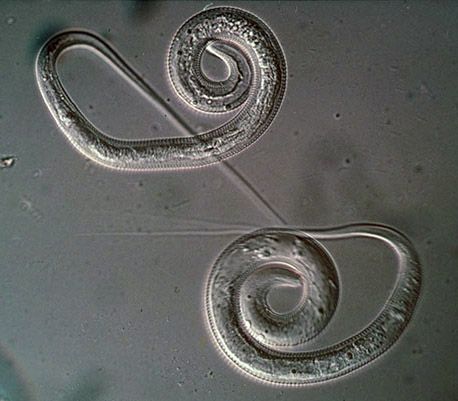
Guinea worm dracunculiasis, often simply called guinea worm disease, is caused by the parasitic worm Dracunculus medinensis. This condition primarily affects those who consume contaminated drinking water containing tiny water fleas harboring the larvae. Once ingested, the larvae grow inside the human body for about a year before emerging through painful blisters.
Historically, this affliction dates back thousands of years. Ancient texts and artifacts reveal its presence in various cultures around the world. The symptoms have left many crippled by discomfort and debilitating pain.
Efforts to understand and combat this parasite gained momentum in the 20th century. With initiatives focused on education and improved sanitation, significant strides have been made toward reducing its prevalence globally. Today, it stands as a reminder of our collective struggle against infectious diseases throughout history.
Causes and Transmission of the Disease
Guinea worm dracunculiasis is primarily caused by the parasite Dracunculus medinensis. This slender, white worm can grow up to three feet long inside a human host. Infection begins when contaminated water containing larvae is consumed.
Once ingested, the larvae penetrate the intestinal wall and mature over several months. After about a year, the female worm emerges painfully from the skin, typically in the lower limbs. This process often leads to secondary infections due to open sores.
Transmission occurs largely through drinking untreated water sources such as ponds or rivers where infected individuals have released larvae into their environment. Communities lacking access to clean water are at higher risk for this disease, highlighting a critical public health issue that affects vulnerable populations around the globe. Understanding these transmission dynamics is crucial for effective prevention efforts aimed at eradicating guinea worm dracunculiasis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of guinea worm dracunculiasis typically surface about a year after infection. Initially, individuals may experience fever, swelling, and pain in the area where the worm is developing.
As the disease progresses, a blister forms, often on the lower extremities. This can be extremely painful and leaves those affected vulnerable to secondary infections.
When the worm emerges from the skin, it creates an open wound that can take weeks to heal completely. The sight of this long white worm protruding from the body is alarming for many.
Diagnosis usually involves identifying these symptoms along with patient history. Health professionals may also examine any visible blisters or ulcers to confirm their findings. Early detection plays a crucial role in managing complications and preventing further spread of this debilitating illness.
Treatment Options for Guinea Worm Dracunculiasis
Treatment for guinea worm dracunculiasis focuses primarily on alleviating symptoms and managing the infection. This parasitic disease does not have a specific medication to kill the adult worms directly.
The most common method involves slowly extracting the worm from the affected area, typically through careful winding around a stick. This process can be painstaking and requires patience, as pulling too quickly may cause the worm to break.
Pain relief is also important. Patients often receive analgesics to manage discomfort associated with inflammation and blisters caused by the worm’s presence.
Preventing secondary infections is crucial as well; healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics if an infection develops at the site of extraction.
Supportive care plays a significant role in recovery, ensuring hydration and nutrition during this challenging time are essential for healing.
Prevention Measures
Preventing guinea worm dracunculiasis starts with access to clean water. Communities need reliable sources of safe drinking water. This significantly reduces the risk of transmission.
Education plays a crucial role in prevention. People must understand how the disease spreads, particularly through contaminated water sources and infected copepods. Awareness campaigns can help communities identify areas at risk.
Filtering drinking water is another effective measure. Using fine mesh filters can catch tiny larvae before they enter the body. It’s a simple yet powerful tool against guinea worm infection.
Health officials also emphasize avoiding open bodies of water during peak seasons when worms are more likely to emerge from ulcers on infected individuals. This helps break the cycle of transmission among community members.
Sustained efforts in sanitation and hygiene are essential too—proper waste management minimizes contamination risks, protecting both personal health and public safety.
The Eradication Efforts of Guinea Worm Dracunculiasis
Efforts to eradicate guinea worm dracunculiasis have gained momentum since the 1980s. Organizations like The Carter Center play a pivotal role in these initiatives. Their commitment has inspired communities worldwide.
Awareness campaigns are crucial. Educational programs inform people about transmission routes and prevention methods. This knowledge empowers individuals to take action against the disease.
The strategy also focuses on providing clean drinking water, essential for breaking the life cycle of the parasite. Community filtration systems have proven effective in reducing infections.
Additionally, surveillance and reporting mechanisms help track cases more accurately. Local health workers engage with affected populations, ensuring timely intervention when necessary.
Innovative technologies continue to emerge, enhancing eradication efforts even further. Collaboration between governments and NGOs strengthens progress toward a guinea worm-free future. Each step taken is a testament to determination and resilience against this preventable disease.
Conclusion
Guinea worm dracunculiasis, a disease caused by the parasitic guinea worm, represents a significant public health challenge. Understanding its history sheds light on how far we have come in combating this affliction. The life cycle of the parasite is intricately linked to contaminated water sources, making education about its transmission vital for prevention.
Symptoms often include intense pain and swelling as the worm emerges from the body, leading to debilitating discomfort. Diagnosis typically involves recognizing these symptoms along with patient history related to water consumption.
While there is no specific treatment that kills the adult worms directly, managing symptoms can help ease suffering. Traditional methods focus on slowly extracting the worm over time.
Prevention remains key in eradicating this disease. Access to clean drinking water and proper sanitation practices are crucial steps toward reducing incidence rates. Community education plays an equally important role in raising awareness about avoiding contaminated water sources.
Efforts led by various organizations aim at complete eradication of guinea worm dracunculiasis worldwide. These initiatives include vaccination programs and partnerships with local communities to ensure sustainable practices are adopted.
The journey toward eliminating guinea worm disease illustrates both challenges and successes in global health efforts today. Continued vigilance and commitment are essential for ensuring future generations live free from this preventable affliction.