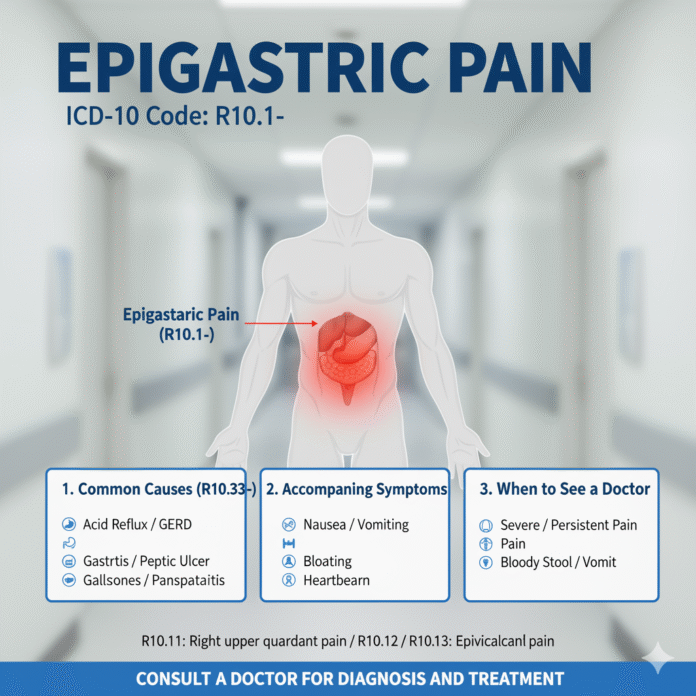
Epigastric pain can be a perplexing experience for many. Located in the upper abdomen, just below the ribcage, this type of discomfort can stem from various causes. Whether it’s a fleeting twinge or a persistent ache, understanding epigastric pain is crucial for both diagnosis and treatment. With the right knowledge, you can identify potential issues and seek appropriate care when necessary. Let’s dive into what you need to know about epigastric pain and its ICD-10 coding system to better equip yourself in managing this condition.
Understanding Epigastric Pain
Epigastric pain refers to discomfort occurring in the upper abdominal region. This area is situated just beneath the ribcage and above the belly button. Many people may experience this type of pain at some point, often leading to confusion about its origins.
The sensation can vary significantly; it might be sharp, dull, constant, or intermittent. Factors such as food intake or stress can influence how this pain feels and when it occurs.
Understanding epigastric pain goes beyond just identifying where it hurts. It’s essential to consider accompanying symptoms like nausea or bloating that could provide clues about underlying issues. Knowing what may trigger your discomfort helps in addressing potential causes effectively.
Common Causes of Epigastric Pain
Epigastric pain can stem from various underlying issues. One common culprit is gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach lining that often results from excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of NSAIDs.
Another frequent cause is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This condition leads to stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus, creating discomfort and a burning sensation.
Peptic ulcers also contribute significantly to epigastric pain. These sores form on the stomach’s interior lining due to H. pylori infection or chronic stress.
Functional dyspepsia may be another factor at play. This syndrome involves persistent upper abdominal discomfort without any identifiable medical cause, leaving many patients frustrated.
Pancreatitis can manifest as severe epigastric pain. Inflammation of the pancreas requires immediate attention and can be triggered by gallstones or alcohol abuse.
Diagnosing Epigastric Pain with ICD-10 Codes
Diagnosing epigastric pain often involves a thorough understanding of the patient’s symptoms and medical history. Healthcare providers utilize ICD-10 codes to classify various conditions, which helps in accurate documentation and treatment.
The relevant ICD-10 codes for epigastric pain include R10.13, specifically designated for abdominal pain localized in the epigastric region. It serves as a useful tool for clinicians to identify potential causes linked to this discomfort.
When assessing patient records, these codes guide practitioners in recognizing patterns related to gastric issues or other underlying health problems. This systematic approach enhances communication among healthcare professionals while ensuring that patients receive appropriate care based on their specific diagnoses.
Comprehensive evaluations may lead to further diagnostic testing like endoscopies or imaging studies, depending on the initial findings associated with the ICD-10 classification.
Treatment Options for Epigastric Pain
Treatment for epigastric pain varies based on the underlying cause. For mild cases, over-the-counter antacids can provide quick relief from discomfort. Medications that reduce stomach acid production may also be beneficial.
If the pain is linked to gastritis or ulcers, a doctor might prescribe proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers. These medications help heal the stomach lining and minimize irritation.
Lifestyle choices play a significant role too. Adjusting your diet to include less spicy and fatty foods can ease symptoms. Incorporating smaller meals throughout the day often helps as well.
For chronic conditions like GERD, ongoing management strategies are essential. This may involve both medication and lifestyle adjustments tailored to individual needs.
In more severe cases, interventions such as endoscopy or surgery could be necessary to address structural issues contributing to the pain.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Epigastric Pain
Making simple lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on managing epigastric pain. Start with your diet. Focus on smaller, more frequent meals instead of large portions. This approach helps ease the burden on your digestive system.
Incorporating fiber-rich foods is essential too. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote better digestion and reduce discomfort.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Avoiding carbonated beverages may also alleviate bloating and gas that contribute to pain.
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role as well. Even moderate exercise such as walking can help enhance digestion and decrease stress levels.
Consider incorporating relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation into your routine. These practices not only help manage stress but can also improve overall gut health, making you feel better both physically and mentally.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Epigastric Pain
Epigastric pain can be alarming, especially if it persists. If you experience severe discomfort that doesn’t fade within a few hours, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
Look out for additional symptoms such as vomiting, fever, or difficulty breathing. These could indicate more serious conditions requiring immediate attention.
If the pain radiates to your shoulder or jaw, seek help quickly; this may signal cardiac issues.
Chronic epigastric pain paired with weight loss or changes in bowel habits should also prompt a visit to your doctor. Early intervention is crucial for effective treatment and peace of mind.
Don’t hesitate to reach out if you feel something isn’t right. Your health deserves priority above all else.
Conclusion
Epigastric pain can indicate various underlying health issues. Understanding its causes and potential treatments is essential for effective management. From gastritis to peptic ulcers, the spectrum of conditions requires careful assessment.
ICD-10 codes play a crucial role in diagnosing these ailments accurately, facilitating appropriate treatment plans. Patients should not overlook lifestyle changes that may alleviate symptoms, such as dietary adjustments and stress management techniques.
Recognizing when to seek medical attention is equally vital. Persistent or severe epigastric pain warrants professional evaluation to rule out serious conditions.
Managing epigastric pain involves a multifaceted approach tailored to individual needs and circumstances, paving the way toward improved gastrointestinal health and overall well-being.