Navigating the world of healthcare coding can feel like deciphering a complex puzzle, especially when it comes to conditions like syncope. As an essential part of modern medicine, ICD-10 provides the framework that helps us understand and manage various health issues effectively. But what exactly is syncope? Why is it crucial to have accurate codes for this condition? In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into everything you need to know about ICD-10 for syncope—unpacking its significance in diagnosis and treatment while also shedding light on common challenges in coding. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or simply curious about medical terminology, this article will equip you with valuable insights into the intricate relationship between ICD-10 and syncope. Let’s get started!
What is Syncope?
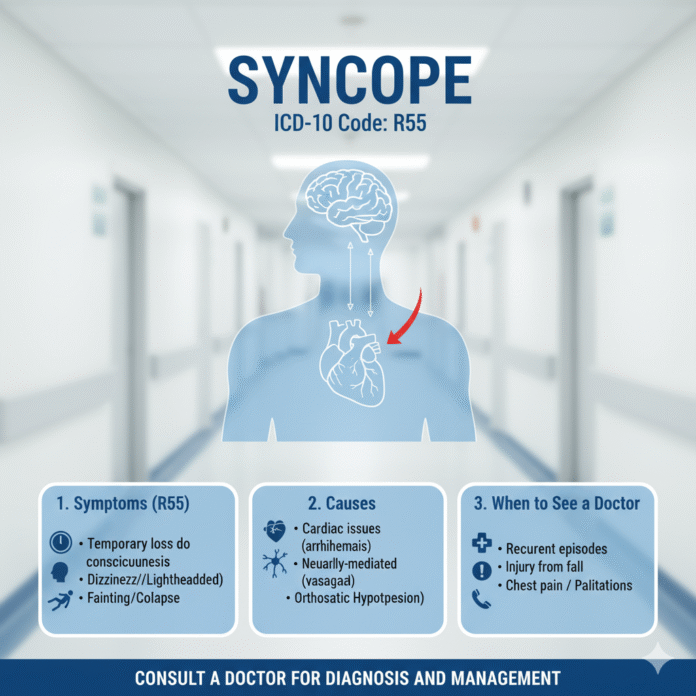
Syncope is a medical term that refers to a temporary loss of consciousness. It often occurs due to insufficient blood flow to the brain.
The most common cause is a sudden drop in blood pressure. This can happen for various reasons, including dehydration or standing up too quickly.
Symptoms typically include dizziness, lightheadedness, and blurred vision before the episode. People may feel disoriented upon regaining consciousness.
While syncope itself is usually brief and harmless, it can sometimes indicate underlying health issues. These could range from heart problems to neurological conditions.
Understanding syncope is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Identifying triggers and patterns can lead to more effective management strategies moving forward.
Understanding the Coding System for Syncope
Understanding the coding system for syncope is crucial for accurate diagnoses and effective treatment. Syncope, or fainting, can arise from various underlying causes, making precise documentation essential.
ICD-10 offers a structured approach to classify these events systematically. Each code provides insights into the specific type of syncope experienced by patients. It ranges from vasovagal episodes to orthostatic hypotension.
Proper coding ensures that healthcare professionals communicate effectively about patient conditions. This clarity aids in research and enhances our understanding of syncope’s prevalence and impact on different populations.
By utilizing correct ICD-10 codes, providers can better track treatments and outcomes over time. This fosters improved care strategies tailored to individual needs while contributing to broader health data analytics within medical facilities.
Mastering this coding system empowers clinicians in their decision-making processes regarding diagnosis and management plans related to syncope cases.
Common Causes and Risk Factors for Syncope
Syncope, often described as fainting or passing out, can stem from various underlying causes. One common trigger is vasovagal syncope, which occurs when the body overreacts to certain triggers like stress or pain.
Other potential culprits include cardiac issues. Arrhythmias and structural heart problems can disrupt blood flow to the brain, leading to a loss of consciousness.
Neurological factors may also play a part. Conditions such as seizures or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) can present with similar symptoms.
Certain medications might contribute to this condition too. Drugs that lower blood pressure or affect heart rhythm could increase the risk of episodes.
Lifestyle choices shouldn’t be overlooked either. Dehydration and prolonged standing in hot environments are frequent contributors to syncopal events. Understanding these causes helps patients manage their health better and seek appropriate care when needed.
ICD-10 Codes for Different Types of Syncope
ICD-10 coding for syncope varies based on its underlying causes and types. Recognizing the specific type is crucial for accurate documentation.
The code R55 represents ‘syncope and collapse.’ This is a catch-all designation that encompasses various scenarios of fainting without pinpointing a cause. It’s often used when the reasons remain unclear after initial assessments.
For more detailed cases, other codes come into play. For instance, G40.409 identifies syncope associated with epilepsy, while I63 categorizes cerebrovascular accidents leading to syncopal events.
Cardiac-related syncopes can be coded under I49.x series, which includes arrhythmias causing loss of consciousness.
These distinctions in ICD-10 codes ensure proper diagnosis tracking and facilitate better patient management strategies tailored to individual needs. Accurate coding impacts treatment plans significantly and helps healthcare providers communicate effectively across disciplines.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Syncope with ICD-10 Codes
Diagnosing syncope involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests. Physicians often rely on ICD-10 codes to categorize the type of syncope observed. This ensures accurate documentation and billing.
Treatment plans vary based on the underlying cause identified during diagnosis. For instance, if a patient experiences reflex syncope due to stress or pain, lifestyle modifications may suffice. On the other hand, patients with cardiac-related syncopes might require medications or even surgical intervention.
Utilizing specific ICD-10 codes helps healthcare providers streamline treatment protocols while ensuring compliance with insurance requirements. Accurate coding can also enhance data collection for research purposes related to syncopal episodes.
By linking symptoms to precise codes like R55 (syncope), clinicians can track trends in diagnoses over time. This contributes significantly to improving overall patient outcomes through better-targeted therapies and interventions.
Challenges and Limitations of Using ICD-10 for Syncope
The use of ICD-10 for syncope presents several challenges. One major issue is the complexity of the coding system itself. With numerous codes available, providers may struggle to select the most accurate one.
Ambiguity in definitions also complicates matters. Syncope can be caused by various underlying conditions, making it difficult to pinpoint a single diagnosis. This often leads to inaccuracies in documentation and potential miscommunication among healthcare professionals.
Another challenge lies in the frequent updates to coding guidelines. Providers must stay informed about changes that could affect their practice, which adds an additional layer of responsibility.
Moreover, variations in clinical practices across different healthcare systems can lead to inconsistent coding practices. These discrepancies may hinder data analysis and impact overall patient care quality as well as research outcomes related to syncope treatment and management.
Tips for Accurate Coding and Documentation
Accurate coding and documentation are essential for effective patient care and proper reimbursement. Start by ensuring you have a solid understanding of the ICD-10 guidelines specific to syncope.
Utilize electronic health records (EHR) that prompt for necessary details. This can minimize errors in coding while ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
Always cross-reference symptoms with appropriate codes before finalizing any entries. Pay attention to even minor variations, as they could significantly impact treatment plans.
Engage in continuous education on updates or changes to ICD-10 codes related to syncope. Regular training sessions can help keep your practice current.
Involve team members in discussions about coding practices. Collaborative efforts can enhance accuracy and promote awareness across the board without duplicating efforts.
Future Developments
As healthcare continues to evolve, so does the coding landscape. The future of ICD-10 for syncope looks promising, with ongoing efforts aimed at enhancing the specificity and accuracy of codes related to this condition.
Developments in digital health technologies could lead to more precise data capture directly from patients during an episode of syncope. This might help clinicians make better-informed decisions based on real-time information.
Additionally, as research advances our understanding of syncope’s various types and causes, we can expect updates to the ICD-10 system that reflect these findings. Improved training programs will also play a crucial role in ensuring healthcare providers are well-equipped with the knowledge necessary for accurate coding.
The integration of artificial intelligence into medical coding is another exciting prospect. AI has the potential to streamline processes by suggesting appropriate codes based on patient histories and clinical notes, thus minimizing errors associated with manual entry.
Furthermore, as telemedicine gains traction, there may be collaborative opportunities between remote monitoring devices and electronic health records (EHRs). Such innovations could enhance how coders document instances of syncope while providing better insights into patient outcomes.
Embracing these advancements will not only improve documentation practices but also elevate patient care standards across the board. Keeping abreast of changes in both technology and best practices within healthcare remains vital for all stakeholders involved in managing conditions like syncope through effective use of ICD-10 coding systems.