Congestive heart failure is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain unaware of its implications. It’s not just a single diagnosis but rather a complex syndrome that can lead to serious health complications if left unmanaged. For healthcare providers and patients alike, understanding the nuances of this condition—including its coding in the medical billing system—plays a crucial role in effective treatment and support.
In the realm of healthcare documentation, ICD-10 codes serve as essential references for diagnosing and managing various conditions. If you’ve ever wondered about the specific code used for congestive heart failure or how it impacts treatment options, you’re in the right place. This article will unravel these details while providing insights into symptoms, diagnoses, treatments, and lifestyle changes that can help those living with this challenging condition manage their health more effectively.
What is Congestive Heart Failure?
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a chronic condition where the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently. This inefficiency leads to a buildup of fluid in the lungs and surrounding tissues, causing discomfort and various health issues.
The heart may weaken over time due to numerous factors such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, or previous heart attacks. As it falters, organs do not receive adequate oxygen-rich blood.
Symptoms often include shortness of breath, fatigue, swollen legs or ankles, and rapid heartbeat. These signs can vary from person to person but generally indicate that the body is not getting enough circulation.
Managing congestive heart failure involves understanding its causes and recognizing early symptoms. The sooner one identifies these warning signs, the better equipped they will be to seek appropriate medical care and improve their quality of life.
Understanding ICD-10 Codes
ICD-10 codes are part of the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. They play a crucial role in healthcare documentation and billing.
These codes help standardize diagnoses across various medical facilities. By using ICD-10, healthcare providers ensure consistent communication regarding patient conditions.
Every code consists of alphanumeric characters that specify different ailments, including their severity and manifestation. For example, congestive heart failure has specific codes to differentiate types and stages.
Understanding these codes is vital for accurate reporting. It impacts insurance claims and patient care management directly.
Medical professionals rely on this coding system to track health trends over time as well. This data drives research and public health initiatives aimed at improving treatment outcomes for various diseases.
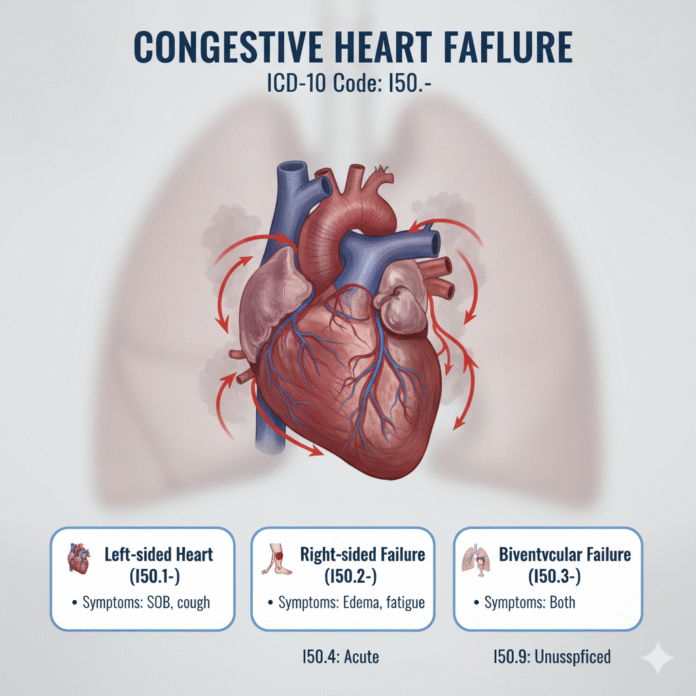
The ICD-10 Code for Congestive Heart Failure
The ICD-10 code for congestive heart failure (CHF) is essential for accurate medical billing and diagnosis. It helps healthcare providers categorize the condition effectively, ensuring proper treatment plans are in place.
There are several codes under this category, including I50.1 for left-sided heart failure and I50.9 for unspecified heart failure. Each code addresses specific manifestations of the disease, making it easier to track patient care.
Using these codes can streamline communication between specialists and primary care providers. This ensures that everyone involved in a patient’s healthcare journey has access to vital information.
Accurate coding also plays a crucial role in research studies related to CHF. It allows researchers to analyze trends and develop better management strategies over time, ultimately improving patient outcomes significantly.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure can manifest through a variety of symptoms, often making it challenging to recognize. Common signs include shortness of breath during routine activities or even at rest. This happens when fluid builds up in the lungs.
Fatigue is another frequent complaint. Patients may find daily tasks exhausting due to decreased blood flow and oxygen supply to muscles.
Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen is also typical. This occurs as excess fluid accumulates in these areas, causing discomfort and weight gain.
A persistent cough may develop too. It might produce frothy sputum that can be alarming for those affected.
Diagnosing congestive heart failure involves a thorough medical history review and physical examination. Doctors often recommend tests like echocardiograms or chest X-rays to assess heart function and fluid levels accurately.
Treatment Options for Congestive Heart Failure
Treatment for congestive heart failure often involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes tailored to the individual.
Common medications include diuretics, which help eliminate excess fluid. ACE inhibitors are also frequently prescribed to lower blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart. Beta-blockers can improve heart function by slowing down the heartbeat.
In some cases, advanced treatments like implantable devices may be necessary. These can include pacemakers or defibrillators that help regulate abnormal heart rhythms.
For those with severe symptoms, surgical options might be explored. This could involve procedures such as valve repair or even a heart transplant in extreme situations.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential for adjusting treatment plans as needed. Monitoring one’s condition closely allows for timely interventions and better management of symptoms over time.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Congestive Heart Failure
Managing congestive heart failure requires more than just medication. Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in improving quality of life.
A heart-healthy diet is essential. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Reducing sodium intake can help control blood pressure and fluid retention.
Regular physical activity is also important. Simple exercises like walking or swimming can strengthen the heart without overexerting it. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
Monitoring weight regularly helps track fluid retention early on. Keeping an eye on daily weight fluctuations can alert patients to potential issues before they escalate.
Stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation can contribute positively to overall well-being. A calm mind supports a healthier body.
Establishing strong support networks with family, friends, or support groups fosters emotional resilience while navigating this condition’s challenges.
Conclusion
Congestive heart failure is a serious condition that requires careful management and attention. Understanding the ICD-10 coding system can help both healthcare providers and patients navigate this complex illness effectively. By recognizing symptoms early, pursuing timely diagnosis, and adhering to treatment plans, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life.
Adopting lifestyle changes plays a crucial role in managing congestive heart failure. Simple modifications such as dietary adjustments, regular exercise tailored to individual capabilities, and stress management techniques can make a substantial difference.
Awareness of the specific ICD-10 codes for congestive heart failure aids in proper documentation and communication within the healthcare system. This knowledge empowers patients to advocate for themselves while also enabling providers to deliver more effective care.
Staying informed about all aspects of congestive heart failure enhances understanding and fosters proactive health practices. Whether you are navigating your own journey or supporting someone else’s, being equipped with accurate information is invaluable on this path toward better health outcomes.