Diabetes mellitus is a term that resonates with many, yet the complexities surrounding it can often leave individuals feeling confused. Whether you’re a healthcare provider, coder, or someone seeking to understand this condition better, grasping the nuances of diabetes and its classification in ICD-10 is essential. Navigating the world of medical coding can be daunting, especially when dealing with such a prevalent health issue. With millions affected by diabetes worldwide, accurate documentation and coding are vital for effective treatment and management. Let’s unravel the intricate relationship between diabetes mellitus and ICD-10 codes to equip you with valuable insights!
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose, a vital source of energy. When functioning properly, insulin regulates blood sugar levels. However, in diabetes, this regulation is disrupted.
There are two primary types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 occurs when the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This form typically arises in childhood or adolescence.
Type 2 diabetes develops over time and often relates to lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. The body either becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it.
Both types lead to elevated blood sugar levels if left unmanaged. Symptoms can include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Understanding these variations helps inform treatment strategies tailored for each individual’s needs.
What is ICD-10 and How Does it Relate to Diabetes?
ICD-10, or the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, is a system used worldwide for coding diagnoses and procedures. It’s crucial in healthcare for tracking health statistics and billing purposes.
When it comes to diabetes mellitus, ICD-10 provides specific codes that help categorize different types of the condition. This classification allows healthcare providers to document patient diagnoses accurately.
Using these standardized codes facilitates better communication among practitioners and ensures appropriate treatment plans are implemented. Accurate coding can also impact insurance reimbursements significantly.
Each type of diabetes has its own unique code within this framework. Understanding these distinctions helps clinicians provide tailored care to their patients while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
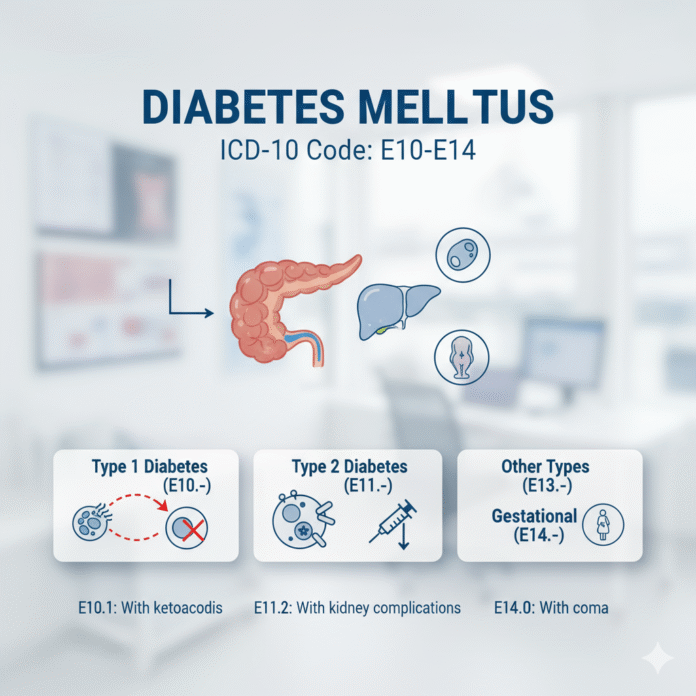
The Different Types of Diabetes Mellitus in ICD-10
Diabetes mellitus is categorized into several types in the ICD-10 system. Each type has distinct characteristics that guide diagnosis and treatment.
Type 1 diabetes, coded as E10, typically arises from an autoimmune response, leading to insulin deficiency. Patients often require lifelong insulin therapy for management.
Type 2 diabetes, designated as E11, accounts for the majority of cases. It usually develops due to insulin resistance combined with relative insulin deficiency. Lifestyle changes and medication are common interventions.
Another category includes gestational diabetes (E13), which occurs during pregnancy. This condition requires careful monitoring to ensure both maternal and fetal health.
There are also specific codes for diabetes complications such as neuropathy or retinopathy under each primary category. These detailed distinctions help healthcare providers accurately document patient conditions and tailor their care effectively.
Diagnosis and Coding Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in ICD-10
Accurate diagnosis and coding of diabetes mellitus in ICD-10 are essential for effective patient care and reimbursement processes. Healthcare providers must be familiar with the specific codes associated with each type of diabetes.
When diagnosing diabetes, it’s crucial to include relevant clinical details. This includes whether the condition is controlled or uncontrolled, as these factors can impact treatment plans.
ICD-10 offers distinct codes for different types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, gestational diabetes, and other specified forms. Each code captures unique characteristics that guide healthcare decisions.
Documenting complications like neuropathy or nephropathy is equally important. These conditions often coexist with diabetes and require their own specific coding.
Following guidelines ensures proper billing practices while enhancing patient outcomes through tailored management strategies. Staying updated on changes to coding rules will also support accuracy in documentation and reporting.
Common Mistakes in Coding for Diabetes Mellitus
Coding for diabetes mellitus can be tricky. Many healthcare professionals make common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate data.
One frequent error is using outdated codes. ICD-10 updates regularly, and it’s vital to stay current with the latest revisions. Using an old code can result in claim denials or incorrect treatment plans.
Another mistake involves not specifying the type of diabetes. Simply coding as “diabetes” without indicating whether it’s type 1 or type 2 can create confusion in patient management.
Omitting complications is also a critical oversight. Diabetes often leads to other health issues like neuropathy or retinopathy, which should be documented accurately for proper care and billing.
Overlooking documentation guidelines may lead to errors as well. Ensuring complete records helps support the chosen codes and enables smoother claims processing.
Tips for Accurate ICD-10 Coding for Diabetes Mellitus
Accurate ICD-10 coding for diabetes mellitus is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Start by familiarizing yourself with the specific codes related to different types of diabetes, such as Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Proper documentation plays a key role. Ensure that physician notes clearly indicate the type of diabetes and any complications present. This clarity helps in selecting the right code.
Stay updated on coding guidelines and changes from CMS or other relevant bodies. Regular training sessions can enhance your understanding of nuances in coding practices.
Utilize specific modifiers when applicable. They provide additional details about comorbid conditions affecting a patient’s health status.
Double-check your work before submission. A second look can catch errors that might otherwise lead to claim denials or discrepancies in patient records.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of diabetes mellitus coding under ICD-10 is essential for healthcare professionals. Understanding the nuances of different types, diagnosis criteria, and accurate coding practices can significantly improve patient care and administrative efficiency. By being aware of common pitfalls in coding, practitioners can avoid errors that could lead to misdiagnoses or inappropriate treatments.
Keeping up-to-date with changes in guidelines ensures compliance and accuracy in documentation. With a thorough grasp of how diabetes is classified within ICD-10, medical coders can enhance their skills while providing quality support to healthcare teams. Mastery over this aspect not only aids individual practice but also contributes positively to broader healthcare outcomes.
This knowledge empowers both providers and patients alike by creating an environment where effective management strategies for diabetes mellitus thrive.